Dear all,
Kindly Check Out skynetconsult.in For More Blog.
Regards,
skynetConsultacy.
ISP Related Blog.
#yum update && yum upgrade# yum install nano wget bzip2
# nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE="eth0"
BOOTPROTO="static"
HWADDR="00:0C:29:01:99:E8"
NM_CONTROLLED="yes"
ONBOOT="yes"
TYPE="Ethernet"
UUID="7345dd1d-f280-4b9b-a760-50208c3ef558"
NAME="eth0"
IPADDR=192.168.1.40
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
GATEWAY=192.168.1.1
DNS1=192.168.1.1
DNS2=8.8.8.8
# nano /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/network
# service network restart
# nano /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 centos.mydomain.lan centos localhost localhost.localdomain
192.168.1.40 centos.mydomain.lan centos
# nano /etc/hostname
centos
Replace your mail domain .# rpm –Uvh http://fedora.mirrors.romtelecom.ro/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
# yum repolist && yum upgrade
# yum install bash-completion
#wget https://bitbucket.org/zhb/iredmail/downloads/iRedMail-1.0-beta1.tar.bz2
# tar xvjf iRedMail-1.0-beta1.tar.bz2
# cd iRedMail-1.0-beta1
# chmod +x iRedMail.sh
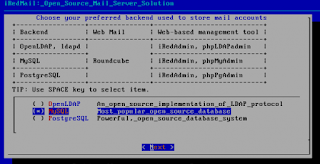
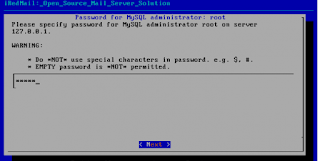
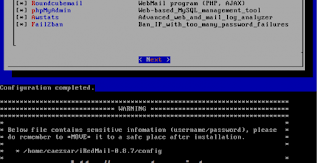
# sudo ./iRedMail.sh
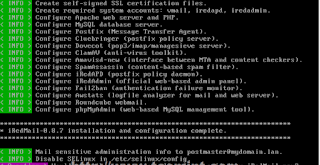
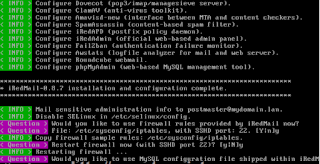
# vi /etc/yum.repos.d/upgrade.repo
Copy and Paste Follow To That file. and Then Press ctrl+o then type :wq to Save and exit from file.[upgrade]
name=upgrade
baseurl=https://buildlogs.centos.org/centos/6/upg/x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
Now Install Following packages.# yum -y install preupgrade-assistant-contents redhat-upgrade-tool preupgrade-assistant
I/O warning : failed to load external entity "/usr/share/openscap/xsl/security-g uide.xsl"
compilation error: file /usr/share/preupgrade/xsl/preup.xsl line 40 element impo rt
xsl:import : unable to load /usr/share/openscap/xsl/security-guide.xsl
I/O warning : failed to load external entity "/usr/share/openscap/xsl/oval-repor t.xsl"
compilation error: file /usr/share/preupgrade/xsl/preup.xsl line 41 element impo rt
xsl:import : unable to load /usr/share/openscap/xsl/oval-report.xsl
I/O warning : failed to load external entity "/usr/share/openscap/xsl/sce-report .xsl"
compilation error: file /usr/share/preupgrade/xsl/preup.xsl line 42 element impo rt
xsl:import : unable to load /usr/share/openscap/xsl/sce-report.xsl
OpenSCAP Error:: Could not parse XSLT file '/usr/share/preupgrade/xsl/preup.xsl' [oscapxml.c:416]
Unable to open file /root/preupgrade/result.html
Usage: preupg [options]
preupg: error: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: '/root/preupgrade/result.htm l'
yum erase openscap
yum install https://buildlogs.centos.org/centos/6/upg/x86_64/Packages/openscap-1.0.8-1.0.1.el6.centos.x86_64.rpm
yum install redhat-upgrade-tool preupgrade-assistant-contentsyum install redhat-upgrade-tool preupgrade-assistant-contents
# preupg
Note: Output of preupg command has been shorted to reduce the length of the post.|System kickstart |notapplicable |
|YUM |notapplicable |
|Check for usage of dangerous range of UID/GIDs |notapplicable |
|Incorrect usage of reserved UID/GIDs |notapplicable |
|NIS ypbind config files back-up |notapplicable |
|NIS Makefile back-up |notapplicable |
|NIS server maps check |notapplicable |
|NIS server MAXUID and MAXGID limits check |notapplicable |
|NIS server config file back-up |notapplicable |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Tarball with results is stored here /root/preupgrade-results/preupg_results-140716022514.tar.gz .
The latest assessment is stored in directory /root/preupgrade .
Upload results to UI by command:
e.g. preupg -u http://127.0.0.1:8099/submit/ -r /root/preupgrade-results/preupg_results-*.tar.gz .
From the above you can find what all are the packages and application will be affected by this upgrade, if you are ok with it; you can go ahead for the next step.cp /root/preupgrade/ /var/www/html/
chmod 0755 /var/www/html/preupgrade/
# rpm --import http://centos.excellmedia.net/7.0.1406/os/x86_64/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
As per the man page, the following command is used to upgrade the CentOS 6; this will download the packages from the internet.# redhat-upgrade-tool --network 7.0 --instrepo http://centos.excellmedia.net/7.0.1406/os/x86_64/
But when i issued the command, it gave me the error to re-run the preupgrade-assistant again. I tried multiple times but no luck.yum install bind bind-utils
vi /etc/named.conf
//
// named.conf
//
// Provided by Red Hat bind package to configure the ISC BIND named(8) DNS
// server as a caching only nameserver (as a localhost DNS resolver only).
//
// See /usr/share/doc/bind*/sample/ for example named configuration files.
//
options {
listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; 192.168.1.1;};
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
allow-query {
any;
};
allow-transfer {
localhost;
192.168.1.0/23;
any;
};
recursion yes;
dnssec-enable yes;
dnssec-validation yes;
/* Path to ISC DLV key */
bindkeys-file "/etc/named.iscdlv.key";
managed-keys-directory "/var/named/dynamic";
forwarders {
8.8.8.8;
};
};
logging {
channel default_debug {
file "data/named.run";
severity dynamic;
};
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
//Forward lookup zone file
zone "skynet.com" {
type master;
file "/var/named/skynet.com.hosts";
};
//Reverse Lookup zone For ip addresses.
zone "2.168.192.in-addr.arpa" {
type master;
file "/var/named/192.168.2.rev";
allow-transfer{192.168.1.1; };
};
//Reverse Lookup Zone For Ip addresses.
zone "1.168.192.in-addr.arpa" {
type master;
file "/var/named/192.168.1.rev";
allow-transfer{192.168.1.1; };
};
$ttl 38400 skynet.com. IN SOA ns1.skynet.com. admin@skynet.com. ( 2018100227 10800 3600 1209600 38400 ) skynet.com. IN NS ns1.skynet.com. skynet.com. IN NS ns2.skynet.com. ns1.skynet.com. 600 IN A 192.168.1.1 ns2.skynet.com. 1200 IN A 192.168.2.1 #secondary System Ip skynet.com. IN A 192.168.1.1 www.skynet.com. IN A 192.168.1.1
$ttl 38400
1.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN SOA skynet.com. admin@skynet.com. (
1498111012
10801
3600
604800
38400 )
1.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN NS ns1.skynet.com.
1.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN NS ns2.skynet.com.
1 IN PTR node-ns1.skynet.com #Replace Your Reverse Lookup. For IP Address 192.168.1.1
$ttl 38400 2.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN SOA skynet.com. admin@skynet.com. ( 1498111012 10801 3600 604800 38400 ) 2.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN NS ns1.skynet.com. 2.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN NS ns2.skynet.com. 1 IN PTR node-ns1.skynet.com #Replace Your Reverse Lookup. For IP Address 192.168.2.1
named-checkconf
service named start
service named enable
Dear all, Kindly Check Out skynetconsult.in For More Blog. Regards, skynetConsultacy.